Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the use of technology to change the genetic makeup of living things for human purposes. Generally, the purpose of biotechnology is to create organisms that are useful to humans or to cure genetic disorders. For example, biotechnology may be used to create crops that resist insect pests or yield more food, or to create new treatments for human diseases.
GENE CLONING Gene cloning is the process of isolating and making copies of a gene. This is useful for many purposes. For example, gene cloning might be used to isolate and make copies of a normal gene for gene therapy. Gene cloning involves four steps: isolation, ligation, transformation, and selection. You can watch an interactive animation about gene cloning at this link:
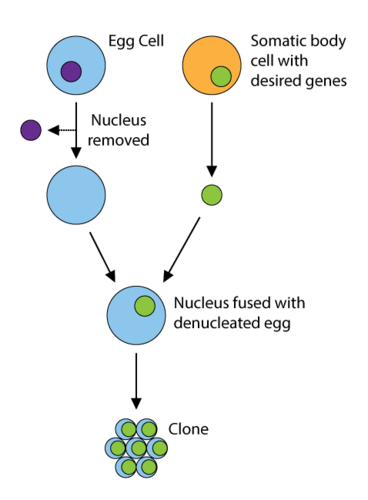
CloningCloning is the process of creating an exact replica of an organism. The clone’s DNA is exactly the same as the parent’s DNA. Bacteria and plants have long been able to clone themselves through asexual reproduction. In animals, however, cloning does not happen naturally. In 1997, that all changed when a sheep named Dolly was the first mammal ever to be successfully cloned. Other animals can now also be cloned in a laboratory.
The process of producing an animal like Dolly starts with a single cell from the animal that is going to be cloned. Below are the steps involved in the process of cloning:
IS CLONING EASY? Cloning is not always successful. Most of the time, this cloning process does not result in a healthy adult animal. The process has to be repeated many times until it works. In fact, 277 tries were needed to produce Dolly. This high failure rate is one reason that human cloning is banned in the United States. In order to produce a cloned human, many attempts would result in the surrogate mothers experiencing miscarriages, stillbirths, or deformities in the infant. There are also many additional ethical considerations related to human cloning. |
BiotechnologyFiles:
practice files will be updated shortly
Helpful linksVocabulary
| ||||||||||||