Gas exchangeWhy do you breathe?
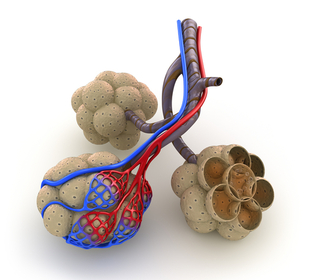
We breathe because we need oxygen. Breathing also releases carbon dioxide from our bodies into the air. The respiratory system is the body system that brings air containing oxygen into the body and releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. How We Breathe? Most of the time, you breathe without thinking about it. Breathing is mostly an involuntary action that is controlled by a part of your brain that also controls your heart beat. If you swim, do yoga, or sing, you know you can control your breathing, however. Taking air into the body through the nose and mouth is called inhalation. Pushing air out of the body through the nose or mouth is called exhalation. How do lungs allow air in? As mentioned above, air moves into and out of the lungs by the movement of muscles. The most important muscle in the process of breathing is the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle that spreads across the bottom of the rib cage. The diaphragm and rib muscles contract and relax to move air into and out of the lungs. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward. The rib muscles contract and cause the ribs to move outward. This causes the chest volume to increase. Because the chest volume is larger, the air pressure inside the lungs is lower than the air pressure outside. This difference in air pressures causes air to be sucked into the lungs. When the diaphragm and rib muscles relax, air is pushed out of the lungs. Exhalation is similar to letting the air out of a balloon. How does the inhaled oxygen get into the bloodstream? The exchange of gasses between the lungs and the blood happens in tiny sacs called alveoli. The walls of the alveoli are very thin and allow gases to pass though them. The alveoli are lined with capillaries. Oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries that surround the alveoli. At the same time, carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction, from capillary blood to the alveoli. BREATHING AND RESPIRATION The process of getting oxygen into the body and releasing carbon dioxide is called respiration. Sometimes breathing is called respiration, but there is much more to respiration than just breathing. Breathing is only the movement of oxygen into the body and carbon dioxide out of the body. The process of respiration also includes the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the cells of the body. Summary
VENTILATION
Respiration begins with ventilation. This is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs. The lungs are the organs in which gas exchange takes place between blood and air.
|
RespirationFiles:
practice files will be updated shortly
Helpful linksHelpful site (thanks jordyn)
breathingVocabularyBreathing Vocabulary
| ||||||