More coming soonThe nervous system, together with the endocrine system, controls all the other organ systems. Controlling muscles and maintaining balance are just two of its roles. The nervous system also lets you:
The nervous system works by sending and receiving electrical signals. The signals are carried by nerves in the body, similar to the wires that carry electricity all over a house. For example, when Michelle started to fall off her scooter, her nervous system sensed that she was losing her balance. It responded by sending messages to muscles in her body. Some muscles tightened while others relaxed. As a result, Michelle’s body became balanced again. source: http://outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/actionpotential_short.swf
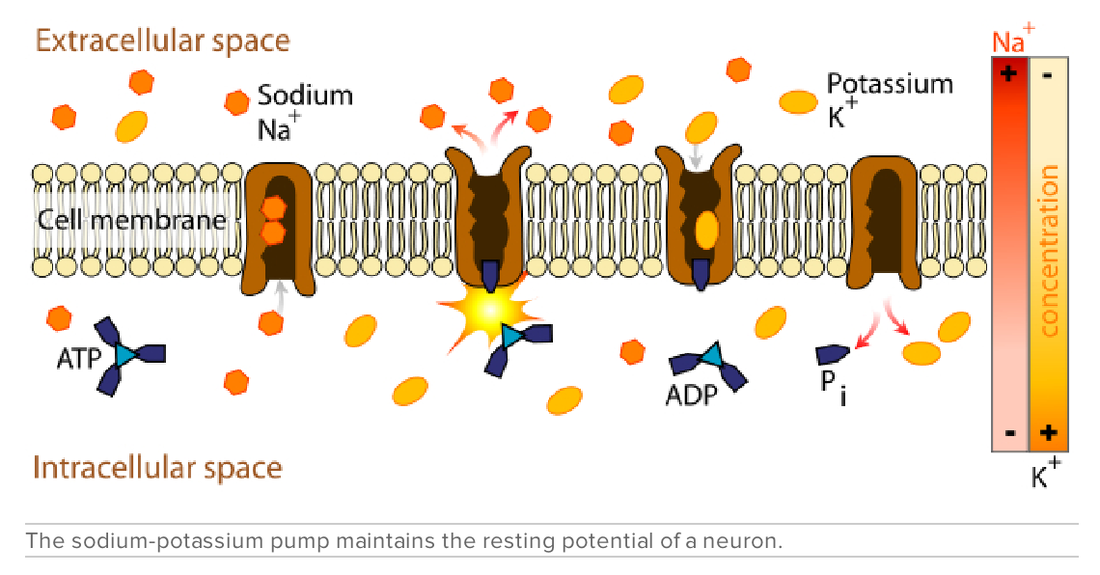
Nerve ImpulsesNerve impulses are electrical in nature. They result from a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
RESTING POTENTIALWhen a neuron is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse. During the resting state, the sodium-potassium pump maintains a difference in charge across the cell membrane. It uses energy in ATP to pump positive sodium ions (Na+) out of the cell and potassium ions (K+) into the cell. As a result, the inside of the neuron is negatively charged, compared to the extracellular fluid surrounding the neuron. This is due to many more positivly charged ions outside the cell compared to inside the cell This difference in electrical charge is called the resting potential. ACTION POTENTIAL
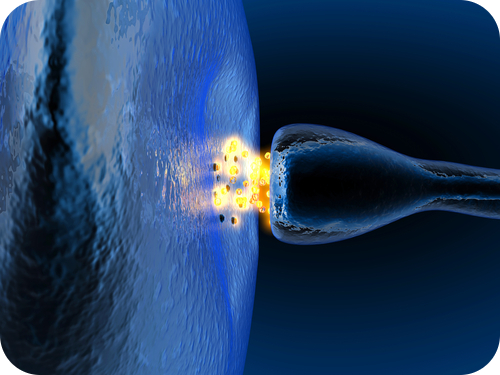
A nerve impulse is a sudden reversal of the electrical charge across the membrane of a resting neuron. The reversal of charge is called an action potential. It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell. The signal causes gates in sodium ion channels to open, allowing positive sodium ions to flow back into the cell. As a result, the inside of the cell becomes positively charged compared to the outside of the cell. This reversal of charge ripples down the axon very rapidly as an electric current . You can watch a detailed animation of an action potential above THE SYNAPSE The place where an axon terminal meets another cell is called a synapse. The axon terminal and other cell are separated by a narrow space known as asynaptic cleft. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, the axon terminal releases molecules of a chemical called a neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter molecules travel across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the membrane of the other cell. If the other cell is a neuron, this starts an action potential in the other cell. |
Nervous systemFiles:Helpful linksPodcasts | ||||||||