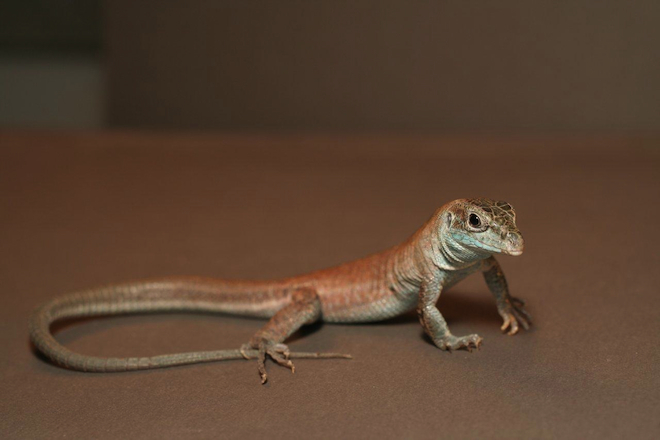
Parthenogenesis
|
Different types of insects, fish, and lizards can reproduce asexually through a process called parthenogenesis. Parthenogenesis happens when an unfertilized egg cell grows into a new organism. The resulting organism has half the amount of genetic material of the parent and without genetic information from another organism it is very similar to the mother.
Parthenogenesis is common in honeybees. In a hive, the unfertilized eggs become drones (males), while the fertilized eggs become workers (females). The queen is a special female that is fed royal jelly during her development. In all cases of parthenogenesis the offspring are nearly identical to one another resulting in very minimal variation. |
The word parthenogenesis comes from the Greek words:
Aphids reproduce sexually during the mating season while males are available, during the non-mating season they give birth to live young that were produced asexually.
|