|
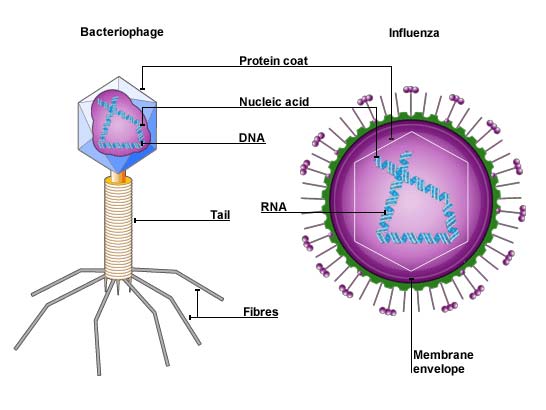
A virus particle, or virion, consists of the following:
|
How a Virus Infects You
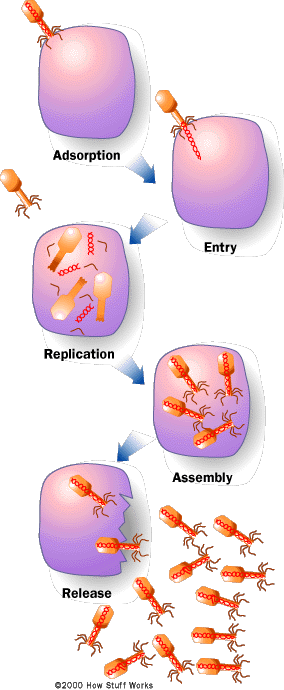
Viruses lie around our environment all of the time just waiting for a host cell to come along. They can enter us through the nose, mouth or breaks in the skin. Once inside, they find a host cell to infect. For example, cold and flu viruses will attack cells that line the respiratory or digestive tracts. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS, attacks the T-cells of the immune system. Regardless of the type of host cell, all viruses follow the same basic steps in what is known as the lytic cycle (see figure):
Those viruses that do not enter the cell must inject their contents (genetic instructions, enzymes) into the host cell. Those viruses that dissolve into a cell simply release their contents once inside the host. In either case, the results are the same. On the Inside Once inside the cell, the viral enzymes take over those enzymes of the host cell and begin making copies of the viral genetic instructions and new viral proteins using the virus's genetic instructions and the cell's enzyme machinery. The new copies of the viral genetic instructions are packaged inside the new protein coats to make new viruses. Once the new viruses are made, they leave the host cell in one of two ways:
The sequence of events that occurs when you come down with the flu or a cold is a good demonstration of how a virus works:
Your immune system responds to the infection, and in the process of fighting, it produces chemicals called pyrogens that cause your body temperature to increase. This fever actually helps you to fight the infection by slowing down the rate of viral reproduction, because most of your body's chemical reactions have an optimal temperature of 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius). If your temperature rises slightly above this, the reactions slow down. This immune response continues until the viruses are eliminated from your body. However, if you sneeze, you can spread thousands of new viruses into the environment to await another host. |
|
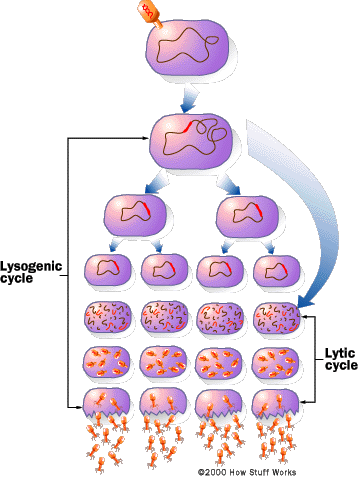
Lysogenic Cycle
Once inside the host cell, some viruses, such as herpes and HIV, do not reproduce right away. Instead, they mix their genetic instructions into the host cell's genetic instructions. When the host cell reproduces, the viral genetic instructions get copied into the host cell's offspring. The host cells may undergo many rounds of reproduction, and then some environmental or predetermined genetic signal will stir the "sleeping" viral instructions. The viral genetic instructions will then take over the host's machinery and make new viruses as described above. This cycle, called the lysogenic cycle, is shown in the accompanying figure. Because a virus is merely a set of genetic instructions surrounded by a protein coat, and because it does not carry out any biochemical reactions of its own, viruses can live for years or longer outside a host cell. Some viruses can "sleep" inside the genetic instructions of the host cells for years before reproducing. For example, a person infected with HIV can live without showing symptoms of AIDS for years, but he or she can still spread the virus to others. |